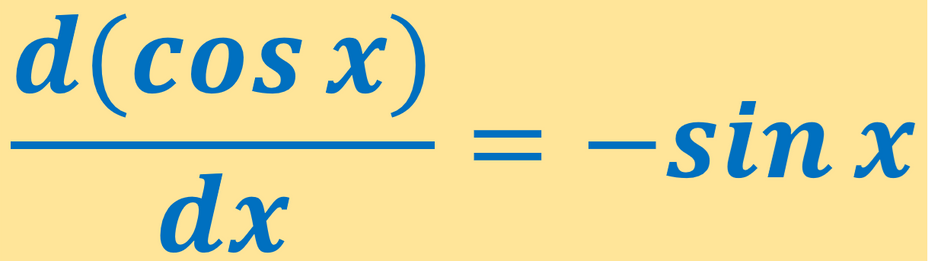The derivative of cos x is -sin x.
What is the Derivative of Cos x ? The derivative of cos x is -sin x.
( cos x ) ′ = − s in x
d x d ( cos x ) = − s in x
Proof of the Derivative of Cos x Way 1 f ′ ( x ) = h → 0 lim h f ( x + h ) − f ( x ) ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos ( x + h ) − cos x cos ( p + q ) = cos p . cos q − s in p . s in q ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos x . cos h − s in x . s in h − cos x
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos x . cos h − cos x − s in x . s in h
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos x . ( cos h − 1 ) − s in x . s in h
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim [ h cos x . ( cos h − 1 ) − h s in x . s in h ]
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos x . ( cos h − 1 ) − h → 0 lim h s in x . s in h
( cos x ) ′ = cos x . h → 0 lim h cos h − 1 − s in x . h → 0 lim h s in h
t → 0 l i m t s in t = 1 t → 0 l i m t cos t − 1 = 0
( cos x ) ′ = cos x .0 − s in x .1
( cos x ) ′ = 0 − s in x
( cos x ) ′ = − s in x
Way 2 f ′ ( x ) = h → 0 lim h f ( x + h ) − f ( x ) ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h cos ( x + h ) − cos x cos p − cos q = − 2. s in 2 p − q . s in 2 p + q ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h − 2. s in 2 x + h − x . s in 2 x + h + x ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h − 2. s in 2 h . s in 2 2 x + h ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h − 2. s in 2 h . s in 2 2 . ( x + 2 h ) ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h − 2. s in 2 h . s in ( x + 2 h ) ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim 2 1 . h − s in 2 h . s in ( x + 2 h ) ( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim 2 h − s in 2 h . s in ( x + 2 h )
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim [ 2 h − s in 2 h . s in ( x + 2 h )]
( cos x ) ′ = h → 0 lim 2 h − s in 2 h . h → 0 lim s in ( x + 2 h )
( cos x ) ′ = − h → 0 lim 2 h s in 2 h . h → 0 lim s in ( x + 2 h )
h → 0 ( 2 h = h )
( cos x ) ′ = − h → 0 lim h s in h . h → 0 lim s in ( x + h ) ( cos x ) ′ = − 1. s in ( x + 0 )
( cos x ) ′ = − 1. s in x
( cos x ) ′ = − s in x
Way 3 s in x = x − 3 ! x 3 + 5 ! x 5 − 7 ! x 7 + 9 ! x 9 − ...
cos x = 1 − 2 ! x 2 + 4 ! x 4 − 6 ! x 6 + 8 ! x 8 − ...
cos x = 1 − 2 ! x 2 + 4 ! x 4 − 6 ! x 6 + 8 ! x 8 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = ( 1 − 2 ! x 2 + 4 ! x 4 − 6 ! x 6 + 8 ! x 8 − ... ) ′
( cos x ) ′ = ( 1 ) ′ − ( 2 ! x 2 ) ′ + ( 4 ! x 4 ) ′ − ( 6 ! x 6 ) ′ + ( 8 ! x 8 ) ′ − ...
( cos x ) ′ = 0 − 2 ! 2 x + 4 ! 4 x 3 − 6 ! 6 x 5 + 8 ! 8 x 7 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = − 2 .1 ! 2 x + 4 .3 ! 4 x 3 − 6 .5 ! 6 x 5 + 8 .7 ! 8 x 7 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = − 1 ! x + 3 ! x 3 − 5 ! x 5 + 7 ! x 7 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = − 1 x + 3 ! x 3 − 5 ! x 5 + 7 ! x 7 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = − x + 3 ! x 3 − 5 ! x 5 + 7 ! x 7 − ...
( cos x ) ′ = − ( x − 3 ! x 3 + 5 ! x 5 − 7 ! x 7 + ... )
( cos x ) ′ = − s in x
Way 4 e i x = cos x + i . s in x
( cos x + i . s in x ) ′ = ( e i x ) ′
( cos x ) ′ + ( i . s in x ) ′ = ( e i x ) ′
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = ( e i x ) ′
( e u ) ′ = u ′ . e u
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = ( i x ) ′ . e i x
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = i . e i x
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = i . ( cos x + i . s in x )
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = i . cos x + i 2 . s in x
i 2 = − 1
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = i . cos x + ( − 1 ) . s in x
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = i . cos x + ( − s in x )
( cos x ) ′ + i . ( s in x ) ′ = − s in x + i . cos x
( cos x ) ′ = − s in x