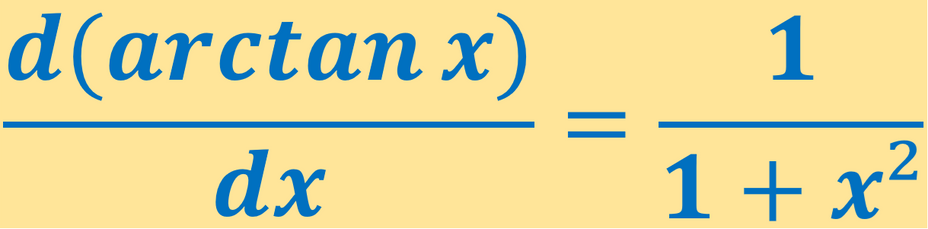La derivada de arctan x es 1/1+x².
¿ Cuál es la Derivada de Arctan x ? La derivada de arctan x es 1/1+x².
( a rc t an x ) ′ = 1 + x 2 1
d x d ( a rc t an x ) = 1 + x 2 1
Prueba de la Derivada de Arctan x Método 1 f ′ ( x ) = h → 0 lim h f ( x + h ) − f ( x )
( a rc t an x ) ′ = h → 0 lim h a rc t an ( x + h ) − a rc t an x
a rc t an ( x + h ) = U , t an U = x + h a rc t an x = V , t an V = x t an U − t an V = x + h − x t an U − t an V = h h → 0 , t an U − t an V → 0 , t an U → t an V , U → V ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U → V lim t an U − t an V U − V t an p − t an q = cos p . cos q s in ( p − q ) ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U → V lim cos U . cos V s in ( U − V ) U − V ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U → V lim [ s in ( U − V ) ( U − V ) . cos U . cos V ] ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U → V lim [ s in ( U − V ) U − V . cos U . cos V ] ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U → V lim s in ( U − V ) U − V . U → V lim cos U . U → V lim cos V U → V , U − V → 0 ( a rc t an x ) ′ = U − V → 0 lim s in ( U − V ) U − V . U → V lim cos U . U → V lim cos V t → 0 l i m s in t t = 1
( a rc t an x ) ′ = 1. cos V . cos V
( a rc t an x ) ′ = co s 2 V
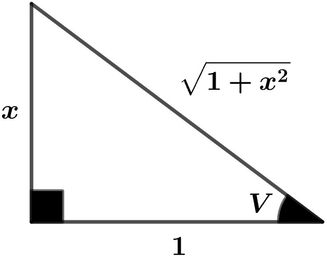
t an V = x
cos V = 1 + x 2 1
( a rc t an x ) ′ = ( 1 + x 2 1 ) 2
( a rc t an x ) ′ = 1 + x 2 1
Método 2 y = a rc t an x
t an y = x
( t an y ) ′ = ( x ) ′
( t an u ) ′ = u ′ . ( 1 + t a n 2 u )
y ′ . ( 1 + t a n 2 y ) = 1
y ′ = 1 + t a n 2 y 1
y ′ = 1 + x 2 1